What is
Experiential Arts?
ex·peri·en·tial: adjective
1. relating to, derived from, or providing experience.
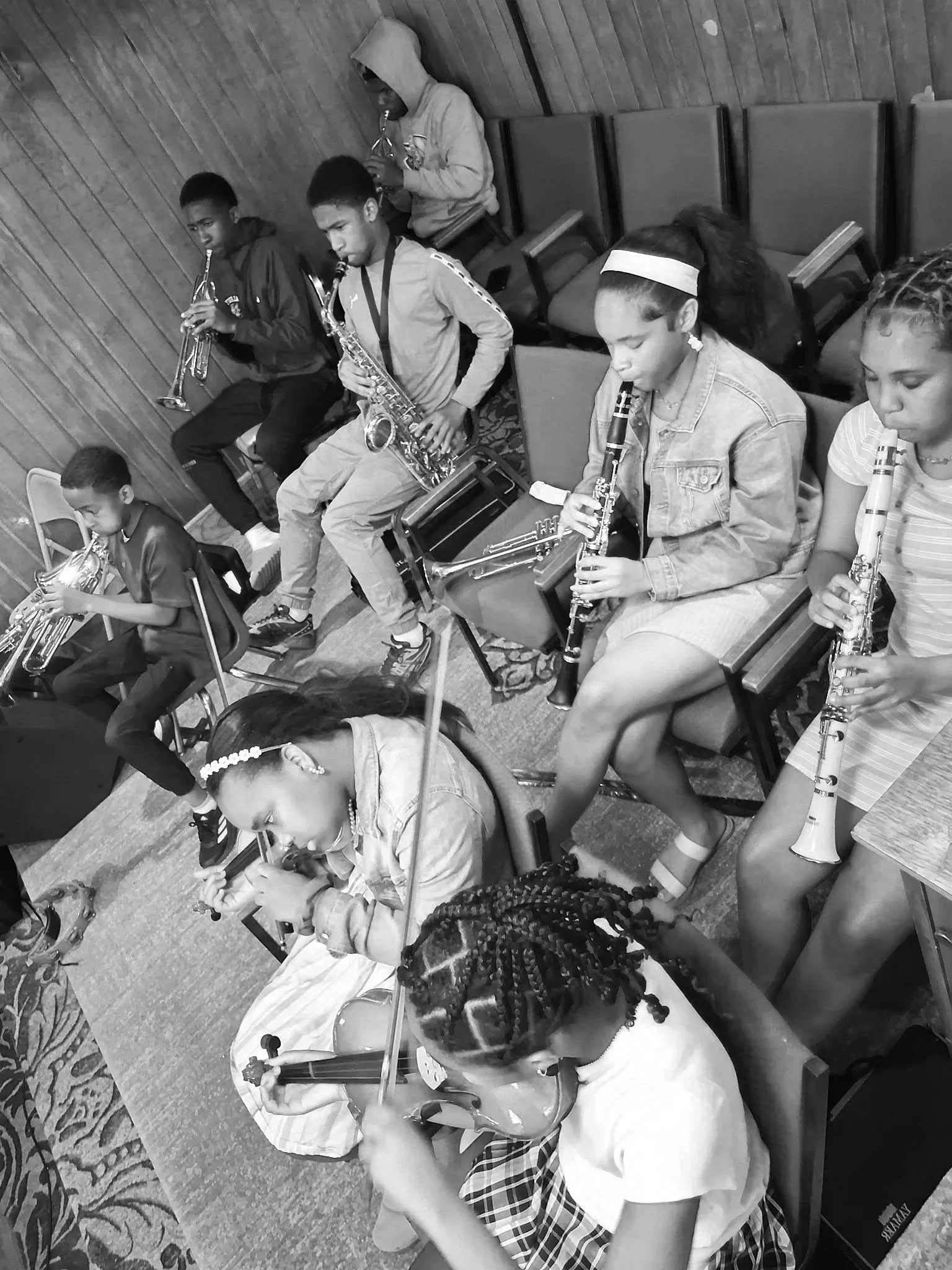
Experiential Arts (EA) is a communal and participatory approach to artmaking that serves to connect communities, reflect cultures, and relate human experiences.
EA prioritizes the “who” and “why” of artmaking, while the “what” and “how” become natural byproducts of the process.
EA breaks the “fourth wall” and invites artists to make art with audiences rather than for audiences, which in turn, engages audiences to become participants in (rather than recipients of) arts experiences.
EA breaks down additional barriers in the arts and arts education as well, including but not limited to: artistic, cultural, socioeconomic, racial, gender, LGBTQ, geographic, and more.
EA can apply to all mediums of art and areas of arts education, and requires minimal resources or expenses to facilitate.
EA embraces emerging advancements in technology such as Artificial Intelligence, and can work with these powerful tools, rather than stand in opposition.
What is
Experiential Learning?
Experiential Learning is a framework for how humans learn, develop, and create meaningful change throughout their lives.
Specifically, NO FEAR’s work is informed and inspired by pioneers in the field of Experiential Learning including John Dewey (Art as Experience), Maxine Greene (Releasing the Imagination), and Paulo Freire (Pedagogy of the Oppressed).
Building off of these influential educators’ work, NO FEAR is developing models for Experiential Arts and Learning that invite young artists to:
Connect: We introduce students to communal and participatory artmaking, so they can learn the experiential and humanizing nature of art early on.
Reflect: We encourage students to share their observations, opinions, and curiosities about art, and then reimagine what they believe to be possible as they become authors of their own artmaking.
Relate: We ask students to share what they find personally relevant and meaningful about art, while to also consider how they can re-interpret their selections and relate their interests to audiences in purposeful and powerful ways.
What are examples of
Experiential Arts?
Participatory Music Performances
Social Dance Practices
Experiential Visual Art
Standup and Improv Comedy
Immersive Theater
Interactive Food and Cooking Demonstrations